About Versavo®
Bevacizumab
Versavo® is bevacizumab biosimilar from Dr. Reddy’s.
Bevacizumab is the first antiangiogenic therapy proven to slow metastatic disease progression in patients with cancer.
It is a humanized recombinant antibody that targets human Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), leading to deterred angiogenesis and tumour growth.[1]
VEGF family and angiogenesis
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was identified in the early 1980s, and is now recognized as an essential regulator of normal and pathological blood vessel growth.[3] Among all the VEGF family members, which includes VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C and PIGF (placenta growth factor), VEGF-A action forms the rate limiting step in blood vessel growth or angiogenesis.[4]
Much before the discovery of VEGF, it was postulated that anti-angiogenesis might be an effective anti-cancer strategy. This led to studies towards developing antibodies that would selectively target VEGF, thereby resulting in dramatic suppression of tumour growth in vivo.[5]
Mechanism of Action
Bevacizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to and neutralizes the activity of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), the key driver of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. This in turn blocks VEGF binding to its cognate receptor on the cell surface, resulting in regression and normalizing of tumour vasculature as well as inhibition of formation of new vasculature, ultimately leading to inhibition of tumour growth.
Indications
Versavo® is indicated for the following:[6]
i. Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mCRC)
Versavo®, in combination with intravenous 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy, is indicated for the first- or second-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
Versavo®, in combination with fluoropyrimidine-irinotecan- or fluoropyrimidine-oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy, is indicated for the second-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who have progressed on a first-line Versavo® containing regimen.
Limitation of Use: Versavo® is not indicated for adjuvant treatment of colon cancer.
ii. First-Line Non-Squamous Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
Versavo®, in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with unresectable, locally advanced, recurrent or metastatic non–squamous non–small cell lung cancer.
Bevacizumab, in combination with erlotinib, is indicated for first-line treatment of adult patients with unresectable advanced, metastatic or recurrent non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) activating mutations.
iii. Recurrent Glioblastoma (GBM)
Versavo® is indicated for the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma in adults.
iv. Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (mRCC)
Versavo®, in combination with interferon alfa, is indicated for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma in adult patients.
v. Persistent, Recurrent, or Metastatic Cervical Cancer
Versavo®, in combination with paclitaxel and cisplatin or paclitaxel and topotecan, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with persistent, recurrent, or metastatic cervical cancer.
vi. Recurrent Epithelial Ovarian, Fallopian Tube, or Primary Peritoneal Cancer
Versavo®, in combination with paclitaxel, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, or topotecan, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with platinum-resistant recurrent epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube or primary peritoneal cancer who received no more than 2 prior chemotherapy regimens.
Versavo®, in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, or with carboplatin and gemcitabine, followed by Bevacizumab as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of patients with platinum sensitive recurrent epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer.
vii. Metastatic Breast Cancer
Versavo® in combination with paclitaxel is indicated for first-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic breast cancer.
Bevacizumab in combination with capecitabine is indicated for first-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic breast cancer in whom treatment with other chemotherapy options including taxanes or anthracyclines is not considered appropriate. Patients who have received taxane and anthracycline containing regimens in the adjuvant setting within the last 12 months should be excluded from treatment with Bevacizumab in combination with capecitabine.
DISEASE BURDEN
Click the button above to know more about the global burden of the disease conditions.
Dosing & Administration
I. Dosing
Versavo® must be administered under the supervision of a physician experienced in the use of antineoplastic medicinal products. Do not administer Versavo® until at least 28 days following surgery and the wound is fully healed. [6]
Posology
i. Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mCRC)
The recommended dose of Versavo® is 5 mg/kg of body weight given once every 14 days as an intravenous infusion. Dose reduction of Versavo® for adverse events is not recommended. If indicated, bevacizumab should either be discontinued or temporarily suspended. The recommended dose when Versavo® is administered in combination with intravenous 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy is:
- 5 mg/kg of body weight every 2 weeks intravenously in combination with bolus-IFL.
- 10 mg/kg of body weight every 2 weeks intravenously in combination with FOLFOX4.
- 5 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks or 7.5 mg/kg or 15 mg/kg of body weight intravenously every 3 weeks in combination with fluoropyrimidine-irinotecan- or fluoropyrimidine-oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients who have progressed on a first-line Versavo®-containing regimen.
It is recommended that treatment be continued until progression of the underlying disease or until unacceptable toxicity.
ii. First-Line Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
The recommended dose is 15 mg/kg of body weight intravenously every 3 weeks in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel.
First-line treatment of non-squamous NSCLC in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy :
Versavo® is administered in addition to platinum-based chemotherapy for up to 6 cycles of treatment followed by Versavo® as a single agent until disease progression.
The recommended dose of Versavo® is 7.5 mg/kg or 15 mg/kg of body weight given once every 3 weeks as an intravenous infusion.
Clinical benefit in NSCLC patients has been demonstrated with both 7.5 mg/kg and 15 mg/kg doses.
It is recommended that treatment be continued until progression of the underlying disease or until unacceptable toxicity.
First-line treatment of non-squamous NSCLC with EGFR activating mutations in combination with erlotinib :
EGFR mutation testing should be performed prior to initiation of treatment with the combination of bevacizumab and erlotinib. It is important that a well-validated and robust methodology is chosen to avoid false negative or false positive determinations.
The recommended dose of bevacizumab when used in addition to erlotinib is 15 mg/kg of body weight given once every 3 weeks as an intravenous infusion.
It is recommended that the treatment with bevacizumab in addition to erlotinib is continued until disease progression.
iii. Recurrent Glioblastoma (GBM)
The recommended dose of Bevacizumab is 10 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks.
iv. Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (mRCC)
The recommended dose of Bevacizumab is 10 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks in combination with interferon alfa.
It is recommended that treatment be continued until progression of the underlying disease or until unacceptable toxicity.
v. Cervical Cancer
Bevacizumab is administered in combination with one of the following chemotherapy regimens: paclitaxel and cisplatin or paclitaxel and topotecan.
The recommended dose of bevacizumab is 15 mg/kg of body weight given once every 3 weeks as an intravenous infusion.
It is recommended that treatment be continued until progression of the underlying disease or until unacceptable toxicity.
vi. Epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube and primary peritoneal cancer
Front-line treatment:
Bevacizumab is administered in addition to carboplatin and paclitaxel for up to 6 cycles of treatment followed by continued use of bevacizumab as single agent until disease progression or for a maximum of 15 months or until unacceptable toxicity, whichever occurs earlier.
The recommended dose of bevacizumab is 15 mg/kg of body weight given once every 3 weeks as an intravenous infusion.
Treatment of platinum-sensitive recurrent disease:
Bevacizumab is administered in combination with either carboplatin and gemcitabine for 6 cycles and up to 10 cycles or in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel for 6 cycles and up to 8 cycles, followed by continued use of bevacizumab as single agent until disease progression. The recommended dose of bevacizumab is 15 mg/kg of body weight given once every 3 weeks as an intravenous infusion.
Treatment of platinum-resistant recurrent disease:
Bevacizumab is administered in combination with one of the following agents – paclitaxel, topotecan (given weekly) or pegylated liposomal doxorubicin. The recommended dose of bevacizumab is 10 mg/kg of body weight given once every 2 weeks as an intravenous infusion. When bevacizumab is administered in combination with topotecan (given on days 1-5, every 3 weeks), the recommended dose of bevacizumab is 15 mg/kg of body weight given once every 3 weeks as an intravenous infusion. It is recommended that treatment be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
vii. Metastatic breast cancer (mBC)
The recommended dose of bevacizumab is 10 mg/kg of body weight given once every 2 weeks or 15 mg/kg of body weight given once every 3 weeks as an intravenous infusion. It is recommended that treatment be continued until progression of the underlying disease or until unacceptable toxicity.
Special populations
Elderly patients: No dose adjustment is required in the elderly.
Patients with renal impairment: The safety and efficacy have not been studied in patients with renal impairment.
Patients with hepatic impairment: The safety and efficacy have not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment.
Paediatric population
The safety and efficacy have not been studied in children.
In published literature reports, cases of non-mandibular osteonecrosis have been observed in patients under the age of 18 years who have received bevacizumab. Bevacizumab is not approved for use in patients under the age of 18 years.
II. Administration
i. Preparation of Solution
Bevacizumab should be prepared by a healthcare professional using aseptic technique to ensure the sterility of the prepared solution.
The necessary amount of bevacizumab should be withdrawn and diluted to the required administration volume with sodium chloride 9 mg/ml (0.9%) solution for injection. The concentration of the final bevacizumab solution should be kept within the range of 1.4 mg/ml to 16.5 mg/ml. In the majority of the occasions the necessary amount of Bevacizumab can be diluted with 0.9 % sodium chloride solution for injection to a total volume of 100 mL.
Parenteral medicinal products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discolouration prior to administration.
ii. Method of administration
The initial dose should be delivered over 90 minutes as an intravenous infusion. If the first infusion is well tolerated, the second infusion may be administered over 60 minutes. If the 60-minute infusion is well tolerated, all subsequent infusions may be administered over 30 minutes.
It should not be administered as an intravenous push or bolus.
Dose reduction for adverse reactions is not recommended. If indicated, therapy should either be permanently discontinued or temporarily suspended. Precautions to be taken before handling or administering the medicinal product
Bevacizumab infusions should not be administered or mixed with glucose solutions.
Bevacizumab is for single-use only, as the product contains no preservatives. Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed in accordance with local requirements.
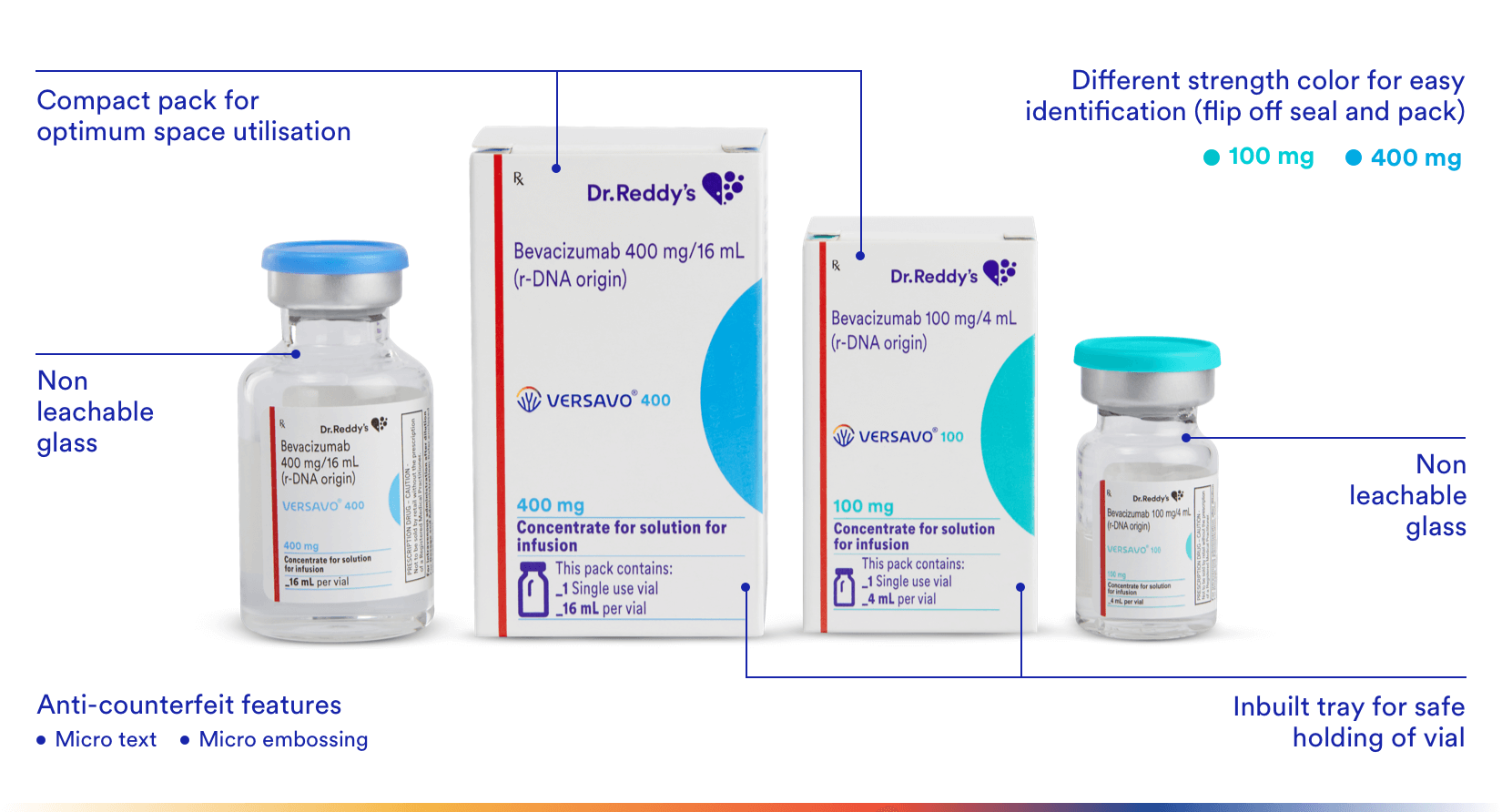
Packaging Benefits
Versavo® (bevacizumab) is available in single use vials (100 mg and 400 mg).
The drug vial and the pack offers unique anti-counterfeit & differentiation features to ensure product integrity & authenticity till it reaches the physicians and patients.
Abbreviations
C1q: complement component 1,q CECs: Circulating endothelial cells, CEPs: circulating endothelial progenitor cells EGFR: endothelial growth factor receptor Fab: fragment antigen binding Fc: fragment crystallizable FcR: Fc gamma receptor FcRn: neonatal Fc receptor GB: Glioblastoma multiforme GI: gastrointestinal HER2: human epidermal growth factor receptor IFL: Irinotecan plus fluorouracil/leucovorin mBC: Metastatic breast cancer mCRC: Metastatic breast cancer mRCC: Metastatic renal cell carcinoma NSCLC: Non-Small cell lung cancer PK: Pharmacokinetics RCT: Randomised clinical trial VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor VEGFR-1: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 VEGFR-2: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2
References
- Ferrara, N., Hillan, K., Gerber, H. and Novotny, W. (2004). Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 3(5), pp.391-400.
- Structure-function relationships of the variable domains of monoclonal antibodies approved for cancer treatment, Journal Article Critical Reviews in Oncology / Hematology; Volume 64, Issue 3; p:210-225; 12/2007; Elsevier; Magdelaine-Beuzelin, C.; Kaas, Q.; Wehbi, V.; Ohresser, M.; Jefferis, R.; Lefranc, M.P.; Watier, H.
- Ferrara, N., & Henzel, W. J. (1989). Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 161(2), 851-858. doi:10.1016/0006-291x(89)92678-8
- Orlandini, M., Marconcini, L., Ferruzzi, R., & Oliviero, S. (1996). Identification of a c-fos-induced gene that is related to the platelet-derived growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor family. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 93(21), 11675-11680. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.21.11675
- Kim, K. J., Li, B., Winer, J., Armanini, M., Gillett, N., Phillips, H. S., & Ferrara, N. (1993). Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Nature, 362(6423), 841-844. doi:10.1038/362841a0
- VERSAVO® (Bevacizumab) Prescribing information, Dr. Reddy’s.